Blocking via Hosts File: 2022’s Best Tips
[ad_1]
You might have heard of a computer’s hosts file. If not, you didn’t miss much. Literally, that’s a file with “hosts” as the name. It has no extension that determines what type of file it is.
So, the file itself is generally inconsequential. However, when placed at a particular location within your computer, it can be an effective tool to control a computer’s access to the outside world — the Internet. In this case, I’d refer to it as the hosts file (cue spooky music).
If you’re interested in a simple and effective way to block certain websites from a computer or are curious about what sort of sorcery this is, you’re reading the right post.
I’ll explain how the hosts file works, its location, and a quick way to edit it on your computer, be it a Windows or a Mac. If you’re a Linux user, chances are you don’t need help editing a random file.
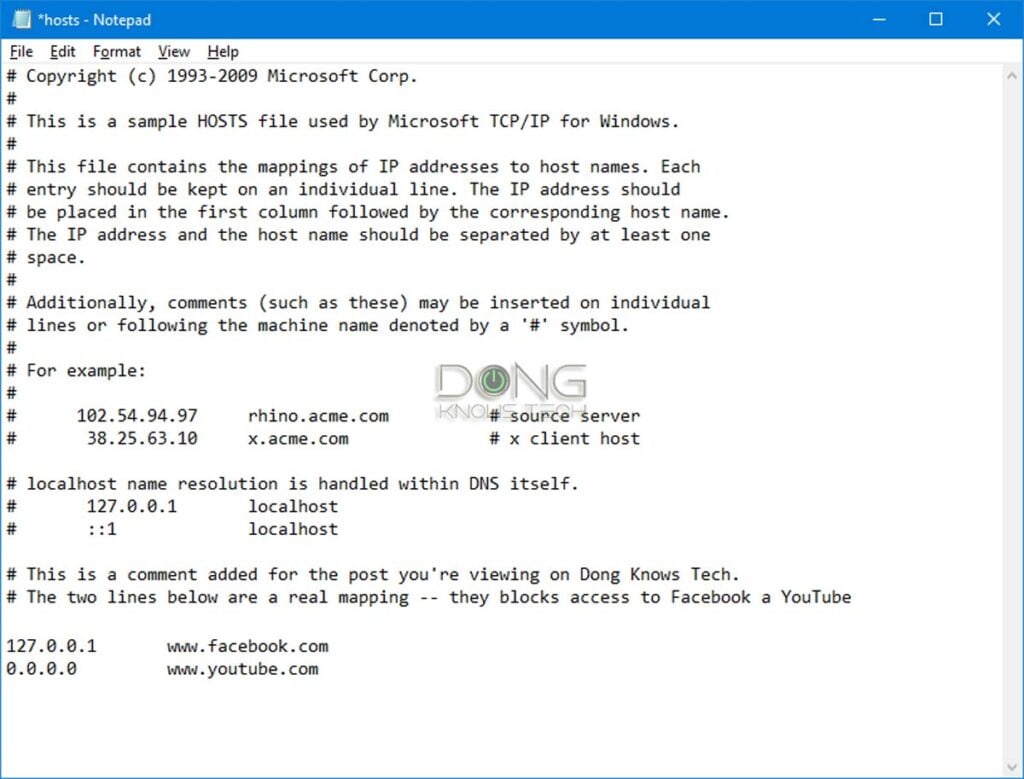
The hash sign (#) in a hosts file signifies commenting.
In programming, commenting is a way to explain what a line of code does without affecting the code itself. The computer ignores the # symbol itself and the text that follows it on each line.
If a hosts file has # at the beginning of every line, which is the default, it’s as good as a blank file from the computer’s perfective.
What is the host file, and how to handle it
Every computer running Windows, macOS, or Linux has its hosts file. By default, this file is not in effect. It’s there, but it doesn’t do anything other than contain brief information on what it is and how to use it.
In other words, you can delete the default hosts file, and nothing will happen. We don’t need it. And we can always recreate it.
Understanding the hosts file
When edited in a certain way, the hosts file works as the computer’s local DNS mapper. It’s a manual way to map a domain, such as facebook.com, to a particular IP address of your choosing.
(The hosts file is the original way of binding a domain with an IP address in the early days of inter-connected computers — the foundation of the Internet — before the DNS server came into existence.)
Extra: DNS server in brief
A DNS server is like a public directory of the Internet. It points you to where you want to go.
(A DNS server is not to be confused with Dynamic DNS, which works somewhat the opposite way.)
Here’s a typical example of the role DNS plays:
Whenever you access a website via its domain name, such as dongknowstech.com, the browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) first queries your DNS server, set by your home router.
This server then looks up the website’s domain name (a.k.a. web address or URL) and returns its IP address, which is a string of seemingly random numbers, to the browser — each website resides at an IP address. The browser then follows that IP address to load the website.
This process is necessary because computers only understand numbers while humans are pretty bad at remembering them. This page appears on your screen because such a process has worked.
In many ways, a DNS server is similar to the once-commonplace telephone directory service, where you only need to remember a person’s name and not their phone number.
So, when you map a domain to a non-existing IP address or that of the computer itself, you effectively block the domain for the computer’s users.
Here’s an example of an entry in a hosts file:
127.0.0.1 www.facebook.com #facebok is a waste of timeThe format of the line is known as the command syntax. In this case, it’s:
IP address (space) domain (space) #(optional)
A couple of things to note:
- The part starting with # is optional. It’s a comment.
- We only need a single space to separate the IP address and the domain, or the domain and the optional comment. But for clarity, you can use multiple spaces or the Tab key on the keyboard.
- The domain should match that of the actual website — some include the “www.” part, others don’t, as in www.facebook.com vs facebook.com. To be sure you can use a separate entry for each.
This particular example entry binds www.facebook.com to the IP of the localhost, the computer itself, and in effect, blocks the computer’s access to Facebook. Specifically, when you go to facebook.com, you’ll get a message that the website doesn’t exist or is unavailable.
Alternatively, you can also use 0.0.0.0 as the IP address to get the same effect. And if you use the IP address of another website, the entry becomes a mean prank or a (malicious) hack.
This mapping takes effect system-wide and immediately, meaning it will affect all user accounts of a computer and you don’t even need to restart the computer.
The way it works, every time you want to reach a domain, such as entering it on a browser, the computer will check its hosts file for the mapping, and if the domain is manually mapped, it’ll use that and no longer query a DNS server for the domain.
And you can manually map as many domains as you’d like — as long as you know what you’re doing and don’t abuse it.
Within the hosts file, each mapping entry (each domain) takes one line. You can map multiple domains to the same IP. So use 0.0.0.0 or 127.0.0.1 if you want to block all of them.
With that, let’s find out where this glorious hosts file resides on your computer and how to edit it.
How to handle the host file on a Windows computer
On a Windows computer, the hosts file always resides at this location:
c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\(In the rare case where Windows is installed on another drive instead of c:, change the drive letter accordingly.)
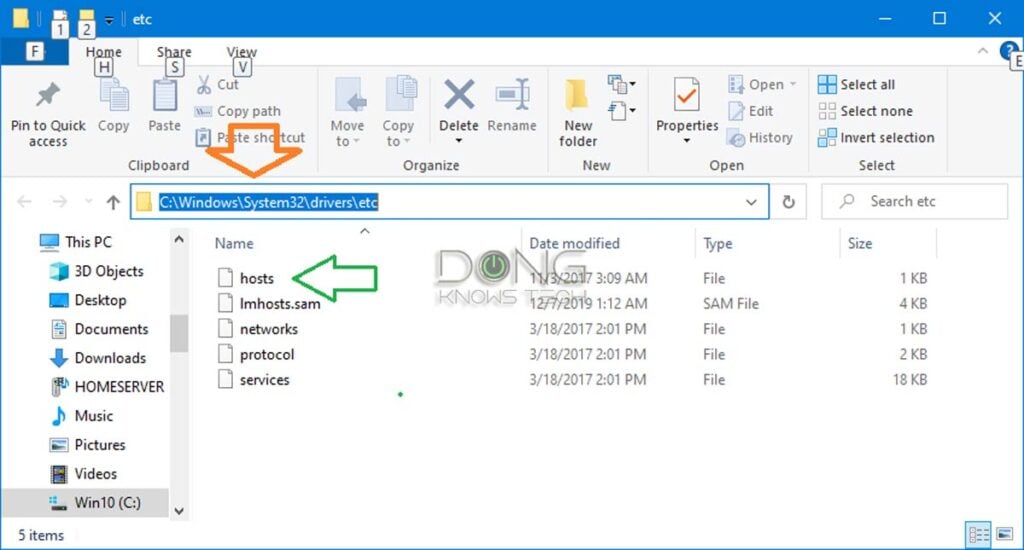
Copy and paste that line onto the address bar of Windows Explorer and hit Enter to quickly get there, as shown in the screenshot above.
Now you can manage the file however you do any file, including deleting, renaming, or making a copy of it. By the way, if you move the host file to another location, it no longer has any effect.
It takes a bit of work to open the host file for editing. Since it has no extension, the usual double-clicking won’t do. Plus, you need to open it with the administrator privilege to be able to make changes.
But generally, you can open it the way you open any file using a text editor, such as Windows’s built-in Notepad app.
If you’re unfamiliar with the app or don’t know how to handle files in general, the fastest way to open the hosts for editing in Windows is to open it via an elevated Command Prompt — again, you won’t be able to save the changes otherwise.
Here are the steps (as shown in the screenshot below).
1. Run elevated Command Prompt
- Type “cmd” (no quotes) into the search field by the Start button
- As Command Prompt appears in the result, right-click on it and choose “Run as administrator”.
- Answer the security prompt, if any, affirmatively.
The Command Prompt window will appear.
2. Open the hosts file in Notepad:
Copy and paste the following command into the Command Prompt window and hit Enter:
notepad c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hostsThat will open the file in Notepad for you to make any changes.
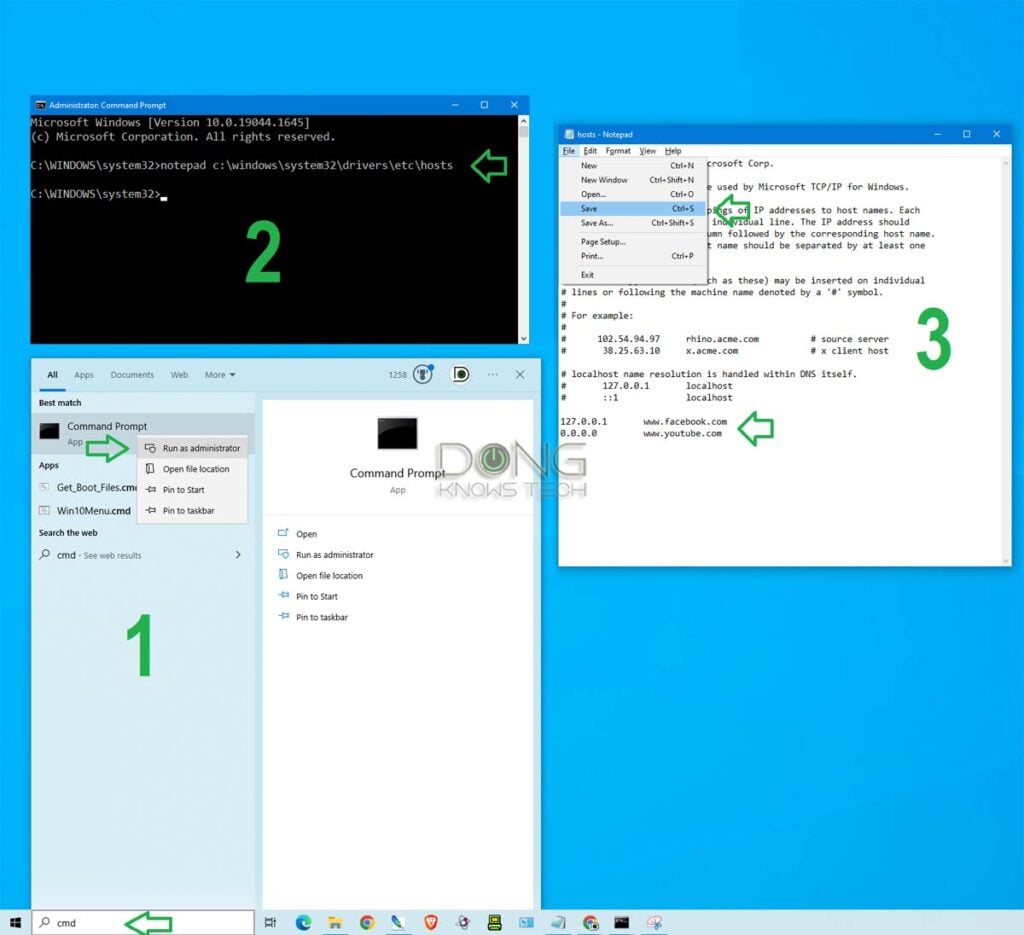
3. Edit the file and save the changes
- Enter domains you want to block following the syntax mentioned above, one domain per line as shown in the last two lines in the screenshot. (Hit Enter each time you want to create a new line.)
- If you no longer want to block a domain, remove the entire line.
Once done, save the file. (Use the Ctrl+S keyboard combo, or just close the file and choose to save when prompted.)
Mission accomplished. The blocking will take effect immediately.
(To test, though, make sure you go to a page of the website that you haven’t visited recently to avoid local caching of the content. Or clear browsing data first.)
***
By the way, the host file shares the same syntax across platforms. Consequently, you can use the same file between Windows and macOS. Or you can copy the content of the file between them.
How to handle the host file on a Mac
The hosts file is located in the /private/etc/ folder on a Mac, which is generally hidden.
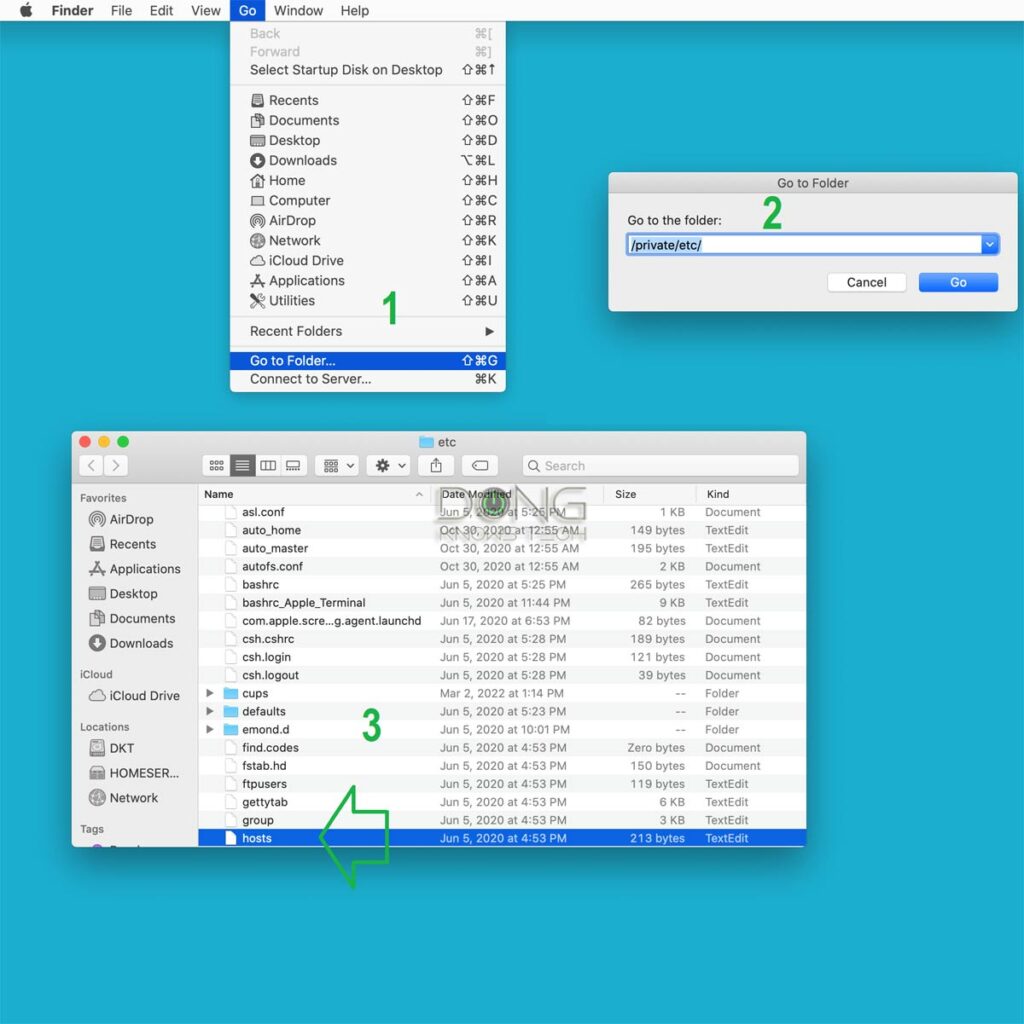
Here are the steps to locate the hosts file on a Mac, as shown in the screenshot above:
- Bring Finder to the forefront by clicking a blank spot on the desktop, then choose Go -> Go to Folder…
- Enter /private/etc/ in the field and hit Go
- Locate the host file in the folder that appears. If it’s not there, you can make a new one or copy one over from another computer.
But if you want to edit the file, you can skip the above.
Here are the step to open the host file on a Mac for editing
- Run Terminal (use the Spotlight to search for it) and enter the following command and press Enter:
sudo nano /etc/hostsYou’ll be asked to enter the password for the account. Do it!
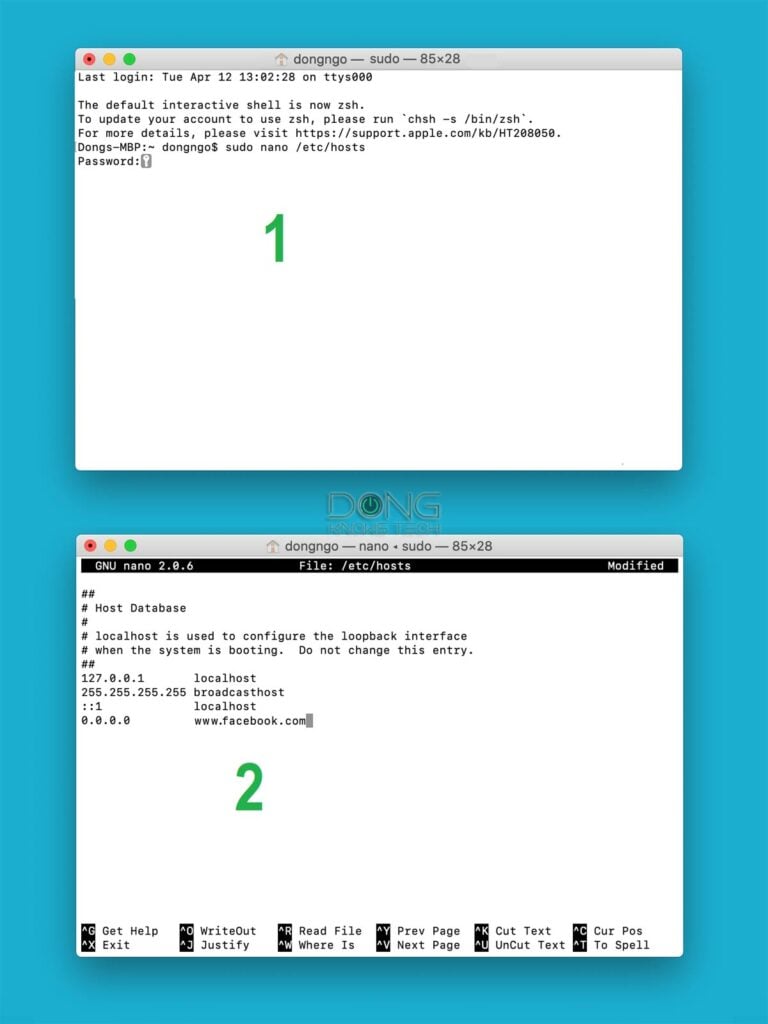
2. The hosts file will be open in the Nano app. You can now use the arrow keys to move around and enter the information as needed.
After that, use Ctrl+0 to save the changes and Ctrl+X to exit. Mission accomplished.
Not a security measure
Before using the host’s file for blocking purposes, ask yourself why you want to block a domain instead of just not visiting it.
No matter what your answer is, this blocking mechanism applies when you want to exert control over something that you don’t have (enough) control over.
Examples are the practice of Parental Control over your child, when you want to give yourself a cushion in controlling the urge to visit websites that you know you shouldn’t, or maybe you just want to mess with, or impress somebody.
The point is the hosts file is not a security measure, it’s a control measure. Blocking a domain doesn’t make your computer any safer, it only keeps the machine from accessing it.
By the way, if I know about the hosts file, which you now do, too, we have to assume that the bad guys also know it. As a result, keep in mind that the file can be used for no-good purposes, considering how easily it can be altered.
The final thoughts
Using the hosts file is the sure way to control the binding of a domain to an IP address in a computer, and all that applies. Consequently, among other things, it’s a straightforward and effective method to block certain websites from the machine.
Entering one domain at a time into the hosts file can be time-consuming. For this reason, there are a lot of pre-made hosts files, where somebody has compiled a long list of blocked domains, available for download.
However, be careful with these pre-packaged hosts files. They tend to include hundreds of domains to block all kinds of things, including legit services.
Many domains are interconnected, and blocking one can make others not work properly. Blocking a wrong domain can also cause important functions of a computer, such as auto-updates or security/integrity checks, to stop working. That’s not to mention there can be malicious entries.
On top of that, a large hosts file can also adversely affect performance. It’s a good idea to keep its size below a few hundred kilobytes.
In short, the hosts file is a good tool when you use it properly, for the right purpose. But it can also be a pain when you abuse it, or are not aware of it.
In any case, it’s a good practice to be mindful of this file and use a blank (default) hosts file when troubleshooting your connection. When in doubt, you can safely disable the file by renaming, deleting, or moving it away from the default location.
[ad_2]
Source link